Archives Hub feature for January 2021
Over the past few years at the Salvation Army International Heritage Centre, we have been working towards digitising parts of our collections in order to provide open access to them online. Our digitisation has been focussed on small, self-contained series of nineteenth-century periodicals and pamphlets from The Salvation Army’s early history. We envisaged these digital collections not only as ways of allowing more people to use and enjoy the material, but also as places where we could put the historical material in context and provide other helpful tools like indices and research guides. As they represent only tiny fraction of our holdings, these digital collections were never intended to be a substitute for accessing our collections in person. However, when in March 2020 we had to close to the public and limit our own access to the archives due to the global response to the COVID-19 pandemic, they unexpectedly became one of the few ways we had of keeping ourselves and others connected with our collections.
Three of the digital collections that we have created so far have now been added to Archives Hub as Online Resources. They are all still works in progress that will continue to grow as we are able to add to them, but this feature provides an introductory overview.
The Darkest England Gazette
In October 1890 — just over 130 years ago — The Salvation Army’s founder William Booth published what is probably his best-known and most influential book, In Darkest England and the Way Out. Planned and researched in under a year while his wife Catherine was terminally ill and released just weeks after her death, the book was penned with substantial assistance from the journalist WT Stead, a family friend and supporter of The Salvation Army’s work. Taking inspiration from the title of Henry Morton Stanley’s In Darkest Africa, published earlier the same year, In Darkest England described the social landscape of the United Kingdom as it had come to be seen by Booth over the course of 25 years of directing The Salvation Army’s evangelistic and social work among people living in poverty.
Booth estimated that a tenth of the country’s population experienced conditions of such extreme misery and destitution that it had become impossible for them to improve their lives without assistance. He called these people ‘the submerged tenth’ and the striking and colourful frontispiece of the book (the work of an unknown artist) shows them struggling to stay afloat in a turbulent sea as waves of hardship (unemployment, starvation, drunkenness, want and sin) crash over their heads. The book set out Booth’s grand plan for rescuing them, which would form the basis for The Salvation Army’s social work going forward. The overarching idea was to reverse the urbanisation that Booth saw as being at the root of so many contemporary social problems by creating a system of ‘colonies’ which would provide shelter, work and support. He intended that people progress through these in a landward direction, starting off in the ‘City Colony’ before moving to the ‘Farm Colony’ and then ultimately to the ‘Colony across the Sea’ where, in the dominant imperial view of the time, open land was considered plentiful and available for the taking.
In Darkest England sold exceptionally well—its first print run sold out on the day of publication and two more editions were printed by the end of the year. Although the reception from readers was mixed, it succeeded in providing the finance and impetus for the rapid expansion of Salvation Army social work and the establishment of many of the institutions Booth had envisaged. The Darkest England Scheme, as The Salvation Army’s organised social work became known, had far-reaching and lasting effects on both The Salvation Army and wider society that have recently been explored in a new anniversary publication, In Darkest England 130 Years On (London: Shield Books, 2020). At the time, however, the Scheme’s objectives and achievements were reported in a weekly newspaper called The Darkest England Gazette which is the subject of one of our digital collections.
The Darkest England Gazette ran from 1 July 1893 to 16 June 1894, after which it continued under the new name The Social Gazette. The Social Gazette soon adopted a smaller, cheaper 4-page format, and it continued to be published in this form until 1917. All 51 issues of The Darkest England Gazette have now been digitised and a growing selection is available online. The digital collection also includes a series of research guides that offer brief introductions to prominent themes from the Gazette which include some quite surprising subjects from animal welfare, vivisection and vegetarianism to poetry and popular fiction.
The Christian Mission
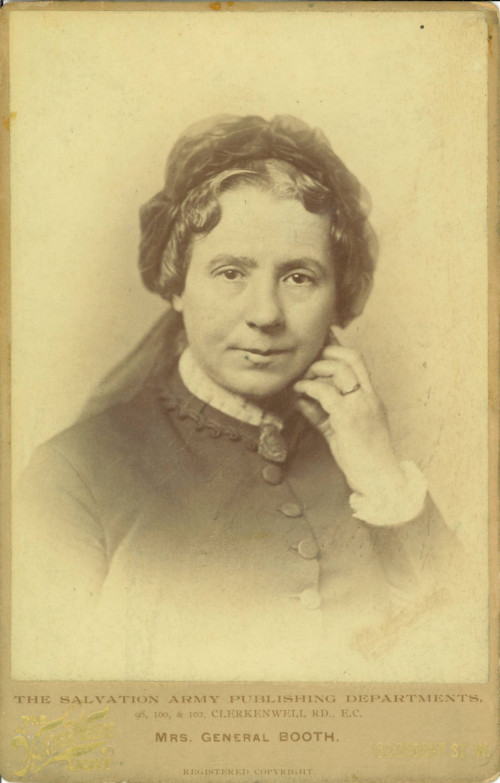
The Salvation Army counts its age from July 1865, but its current name was not adopted until 1878. For most of the first 13 years of its existence it was known as The Christian Mission. The Mission grew out of the East London Special Services Committee, a group of Christian businessmen who did evangelistic work in the east end of London. William Booth, a former Methodist turned independent evangelist, first had contact with this committee in June 1865, when he preached at a meeting organised by them at the Quaker Burial Ground in Whitechapel. Within a short time, he had been asked to give permanent leadership to their ministry and over subsequent decades, grew it into an international movement.
From October 1868, the Mission began publicising its work by means of its own monthly magazine, which ran until it was superseded by the well-known War Cry in December 1879. This magazine is one of the most important surviving sources of information about the early development of The Salvation Army and its expansion from the east end of London throughout the UK. We have now put many issues online alongside a selection of other documents produced by the Mission.
Rare pamphlets
As our other digital collections show, since its earliest days as the Christian Mission (and even before), The Salvation Army’s leaders and members have been prolific publishers, not only of periodicals and books, but also of various forms of pamphlet. One of the earliest in our collection is an 1870 edition of Catherine Booth’s treatise Female Ministry, or Women’s Right to Preach the Gospel, which is a revised version of her 1859 pamphlet Female Teaching. No known copies of the first edition survive but a second edition of her original text dating from 1861 survives in the John Rylands Library at Manchester University. Catherine’s views shaped The Salvation Army’s position on women preachers, whose equal status with their male counterparts has been written into the organisation’s constitution since 1870.
This pamphlet and more than seventy others are now accessible online in our Rare Pamphlets Collection, covering a wide variety of subjects from slum ministry and social work, to international missionary work, to biographies and songs.
Ruth Macdonald
Archivist & Deputy Director
The Salvation Army International Heritage Centre
Twitter & Instagram: @salvarmyarchive
Related
‘The Darkest England Gazette’ Digital Collection
The Christian Mission Digital Collection
Salvation Army Rare Pamphlets Collection
Browse all Salvation Army International Heritage Centre Archive collections on the Archives Hub
Browse all Online Resources descriptions on the Archives Hub
Previous features on the Salvation Army International Heritage Centre’s Archive collections:
Personal diaries in the archive of The Salvation Army International Heritage Centre
Researching 150 years of Salvation Army history
All images copyright Salvation Army International Heritage Centre. Reproduced with the kind permission of the copyright holders.