Archives Hub feature for June 2024
Introduction
Oxford House was founded in 1884 as a ‘settlement house’ for graduates of the University of Oxford volunteering in East London. To celebrate our 140th anniversary, Oxford House has been working for two years on a National Lottery Funded Project to celebrate this anniversary, ‘Through the Lens: Women Pioneers, Youth Social Action and Celebrating Our Somali Community.’ This has involved zine-making with local students, running local photography exhibitions, recording new oral histories with community members who have contributed to the history of the house, and the mammoth task of cataloguing and digitising our archive.
While some of our material is still housed at Tower Hamlets Local History Library and Archives,10,000 pages of archives are now accessible on our new website, available to the wider public for the very first time. This material ranges from our Victorian arrivals book, documenting the movement of students in and out of the building, to 1970s campaign posters created by activist groups who used Oxford House as their base to advocate for change and propose innovative and groundbreaking social schemes. Alongside these are a rich photographic archive which documents the heart of Oxford House throughout its lifetime – its people.
Our Founders
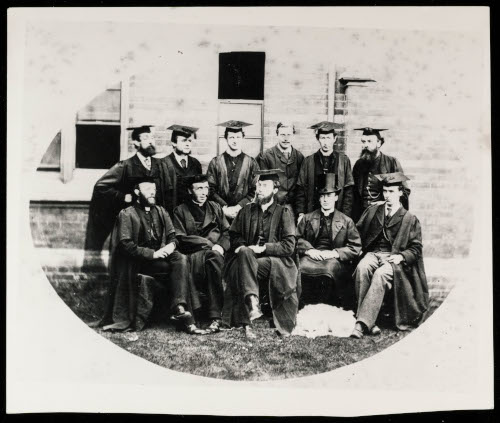

Though, as ‘settlement’ implies, there was indeed an undeniably strong vein of paternalism to educate the lower classes, the reformist social movement sought to provide practical support to the community of East London, such as legal advice and labour exchanges. Our archive is flush with records that set out the early aims for the house – ‘to provide a centre for religious, social, and educational work among the poor of East London.’ One of the most evocative items from our early collection is our arrivals and departures book. Dated from 1910-1938, this was where many from Oxford and beyond noted their comings and goings. It captures the energy of not only the house but of the interest in the wider settlement movement from both a national and international audience, with entries from visitors hailing from New York, Copenhagen, Zurich, and Port of Spain Trinidad.
World War Two
Our records from the WWII era are especially poignant. Located in heavily bombed East London, Oxford House acted as a shelter for up to 300 members of the local community at the height of the Blitz. Away from the East End, Oxford House organised the evacuation of local children to free boarding schools in Wales and Herefordshire, where many city-born children visited the countryside for the first time. While there are few photographs from the inside of the house during this period, Annual Reports from our archive capture the spirit of the time. ‘The House and all that for which it stands shall not die, but shall blossom in the future from the new life which has been born in it during this year of suffering,’ wrote Chairman Walter H. Moberly in 1941.
During this time, Oxford House continued to run clubs and events for members of the community who remained in East London – from sport activities to dance evenings. Significantly, it was during this period that women became an increased presence within the public life of the house. Women have always played a role at Oxford House, yet our early archive often records them only as unnamed domestic servants under ‘housekeeper’ or the like. Molly Clutton-Brock, a campaigner and the wife of the Head of House, Guy Clutton-Brock, took a lead on establishing clubs for women and girls during the war. This was a marked change as Oxford House transitioned post-war from a male-dominated settlement house to a community centre model.
Post-War Social Action
Some of our most dynamic archival records date to the post-war period, when by the 1970s, the East End was buzzing with community spirit and activism. Oxford House was home to many campaigns and social groups, and our archive has a wealth of photographs and posters from this era – as pictured, for example, a health stall hosted in our Cafe where the community could come to receive health advice and information. The Oxford House Social Club and the Oxford House Youth Club were both set up in this era, and our archive once again has a fantastic collection of photographs of activities, events and festivals hosted in and beyond Oxford House.

Our archive also holds the records of many social action campaigns from the late 20th century to present – such as the Tower Hamlets International Solidarity campaign (THIS) 1981-1988 collection, the Families Unit 1977-1981 collection, and the Somali Projects 1985-2023 collection. East London’s Somali community has played a long-standing significant role at Oxford House, with the establishment of Somali Week Festival and the Somali Arts Project designed to platform the creativity and culture of refugees and migrants who came to the East End.
Our NHLF project and 140th Anniversary celebration is culminating in an exhibition, History House. Items from our archive throughout the decades will be exhibited for the first time to share untold stories of the house and those who have worked here and called it home throughout time. We would love for you to visit.
Emily Hughes
Archivist, Oxford House in Bethnal Green
History House is open 6th June – 20th December 2024, Monday to Friday 10am-5pm, at Oxford House in Bethnal Green, E2 6HG. Our archives are open by appointment, please email OHarchive@oxfordhouse.org.uk.
Related
Oxford House Archive, 1898 to present day
Images copyright Oxford House and Tower Hamlets Local History Library and Archive. Reproduced with the kind permission of the copyright holders.