This blog post forms part of History Day 2022, a day of online interactive events for students, researchers and history enthusiasts to explore library, museum, archive and history collections across the UK and beyond. History Day is part of the Being Human festival, the UK’s national festival of the humanities, taking place 10–19 November 2022.
Use Archives Hub, a free resource, to find unique sources for your research, both physical and digital. Search across descriptions of archives, held at over 380 institutions and organisations across the UK.
This year’s History Day is themed ‘Human Discovery: Experiencing Science’, so we’re highlighting a range of archive collections relating to inventions, technology, medical advances and more.

Press photograph of women factory workers during WW1. Image copyright © Institution of Mechanical Engineers.
Feature: Engineering and innovation during the First World War (October 2014).
Inventions and inventors
John Logie Baird papers (1906-2009). Baird was born in Helensburgh and studied electrical engineering at the Glasgow and West of Scotland Technical College, then attended Glasgow University. After becoming apprenticed with Argyll Motors and then to working with other firms, from 1916 he engaged in various private business ventures in Glasgow, London and the West Indies. In 1922 he began to experiment with transmitting and receiving visual signals. In 1924 his efforts were rewarded by a flickering image on his screen. A public demonstration was given at Selfridge’s Oxford Street store in April 1925 and showed the transmission of crude outlines of simple objects. The world’s first demonstration of television followed on 26 January 1926 at the Royal Institution, London. In May 1927 the first demonstration of television between London and Glasgow took place, and in February of the following year the first transatlantic television broadcast was successfully carried out. On 30 September 1929 the BBC made its first television broadcast using the Baird 30-line system. Material held by University of Strathclyde Archives and Special Collections – see full collection description.
Papers of Marjorie Jean Oswald Kennedy (19th-20th century). Marjorie hailed from the Kennedy family of Kilmarnock which included Thomas Kennedy c1796-1874, founder of Glenfield & Kennedy (producers of valves) and inventor of the world’s first water meter. During the Second World War, Kennedy served with the Women’s Royal Naval Service (WRNS), 1942-1945. She was stationed at HMS Pembroke III, the WRNS training depot at Mill Hill in 1942, then at HMS Beaver, Hull, from 1942 to 1943, at HMS Drake, Devonport, in 1943, and then at HMS Pembroke III again and HMS Pembroke V, Bletchley Park, between 1943 and 1945. At Bletchley Park Kennedy was working with the team of allied codebreakers who were able to decrypt a vast number of messages that had been enciphered using the German’s Enigma machine. The intelligence gleaned from this source, codenamed ‘Ultra’ by the British, had been a substantial aid to the Allied war effort. Material held by Edinburgh University Library Special Collections – see full collection description.

Frederick Lanchester at the wheel of the 8 h.p. two cylinder Lanchester known as the ‘Gold Medal Phaeton’ with his brother George as passenger. c1899. Coventry University [reference no. LAN/1/16/4].
Photograph copyright © Coventry University.
Feature: The Frederick Lanchester archive at Coventry University (December 2018):
The work of car manufacturer, engineer, scientist and inventor Frederick Lanchester (1868-1946) is being celebrated by the Lanchester Interactive Archive project at Coventry University. He was one of the UK’s leading automobile engineers of the late 19th and early 20th centuries and creator in 1895 of the first all-British four-wheel petrol driven motor car.
Records, publications and artefacts relating to James Watt (1705-1990): Watt was born at Greenock in 1736. He trained as an instrument maker in London and began to practise this trade in Glasgow. Watt soon developed a reputation as a high quality engineer and was employed on the Forth & Clyde Canal and the Caledonian Canal. In 1763 he repaired the model of Newcomen’s steam engine belonging to Glasgow University, and began experiments on properties of steam. Watt improved on the engine’s design and took out a patent for the separate condenser in 1769. He later adapted the engine to rotary motion, making it suitable for a variety of industrial purposes, and invented the flywheel and the governor. In 1774 he went into partnership with Matthew Boulton to make steam engines at their works at Soho, Birmingham. The first engines were used in collieries and iron works and were the driving force behind the transformation of cotton spinning from a cottage to factory industry. Watt’s inventive talents led him to patent a variety of machines and devices including a letter-copier and a smoke-consuming furnace. Material held by Heriot-Watt University Museum and Archive – see full collection description.
Technology

Lithograph of George Biggin, Letitia Sage and Vincenzo Lunardi ascending from St George’s Fields, London, 29 June 1785. Image copyright © National Aerospace Library.
Feature: Planes, pilots and politics: National Aerospace Library’s collections fly onto Archives Hub (April 2020).
Private Telegraph Companies (1846-1899): The development of the telegraph system in the United Kingdom closely followed the growth of the railways with telegraph offices often being located at stations. The Government allowed the network to develop under private ownership and did not intervene significantly in its running. This was in sharp contrast to the telegraph system on the Continent which had been under state ownership since its inception. By 1868 there were five major telegraph companies operating the inland network, all of which were open to criticism regarding errors, delays and high prices. Frank Ives Scudamore campaigned on behalf of the Post Office for them to be nationalised citing how unfavourably they compared with those on the Continent. Despite protestations from the companies a series of Acts of Parliament were passed and the inland telegraph system came under control of the Post Office in 1870. Material held by British Telecom Archives – see full collection description.
Online Resource: Developing LEO: The world’s first business computer. Reports, memoranda, photographs and other documents from the archives of the statistician John Simmons (1902-1985), including key material on the development of the pioneering LEO computers by J. Lyons & Company Ltd. during the 1940s and 1950s. Provided by Modern Records Centre, University of Warwick.

Barclaycard 1972 promotions. Photograph copyright © Barclays Group Archives.
Feature: Barclaycard: 50 years of plastic money – the story from the Archives (June 2016).

Illustration: Spare Rib, April 1978, photo copyright © The Women’s Library.
Feature: Typewriters and Office Machines
Online Resource: Hiroshima Archive – the Hiroshima Archive is a pluralistic digital archive using the digital earth to display in a multi-layered way all the materials gained from such sources as the Hiroshima Peace Memorial Museum, the Hiroshima Jogakuin Gaines Association, and the Hachioji Hibakusha (A-bomb Survivors) Association. Beyond time and space, the user can get a panoramic view over Hiroshima to browse survivors’ accounts, photos, maps, and other materials as of 1945, together with aerial photos, 3D topographical data, and building models as of 2010. The archive aims to promote multifaceted and comprehensive understanding of the reality of atomic bombing. Stories of Atomic bomb survivors living across Japan. Around 170 testimonies and around 150 photographs can be browsed.
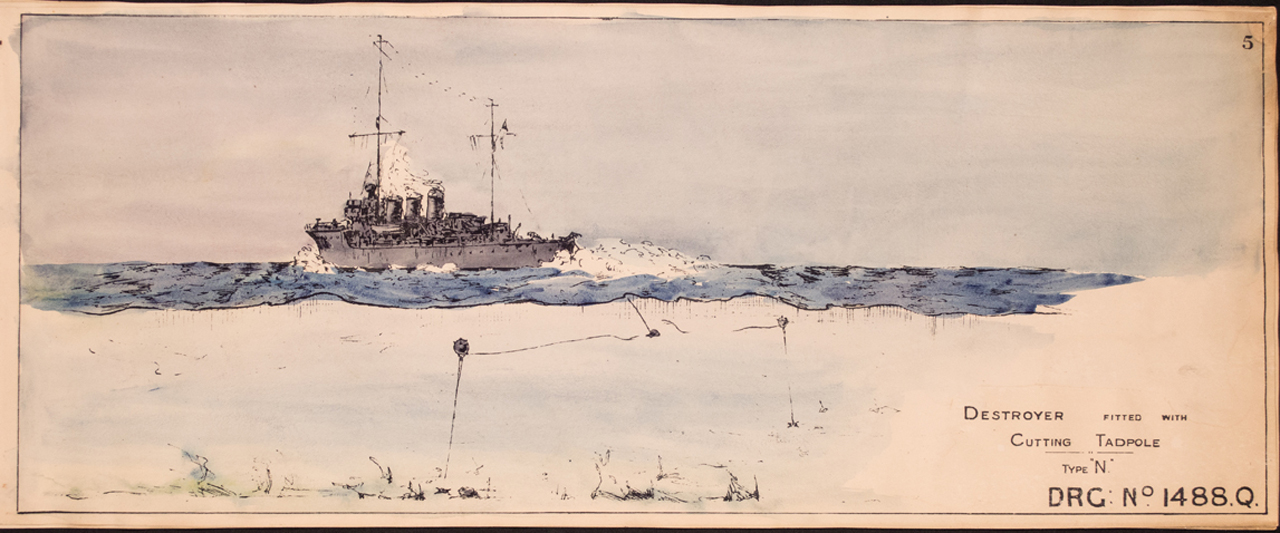
Medical Advances
Papers of the Dorset House School of Occupational Therapy (1919-2005): Dorset House, the first School of Occupational Therapy in England, was established by its visionary Medical Director, Dr Elizabeth Casson, in the latter part of the 1920s. Over the years the School has moved from its original base in Bristol to Bromsgrove, and finally to Oxford, firstly in Nissen Huts in the grounds of the Churchill Hospital and then to London Road in 1964. In 1992 Dorset House School of Occupational Therapy became part of Oxford Polytechnic, which, later that year, was conferred with university status and was named Oxford Brookes University. Material held by Oxford Brookes University Special Collections and Archives – full collection description.

John Charnley/William Waugh Collection (1922-1989): John Charnley, orthopaedic surgeon, born in 1911, was educated at the Medical School of the Victoria University of Manchester. In 1937, he took up his first post as a resident surgical officer at Salford Royal Hospital, and demonstrated an early talent for making and developing specialist apparatus and equipment. He first encountered work in orthopaedics and fractures in 1939 as resident casualty officer at the Manchester Royal Infirmary. During the Second World War, Charnley worked at an Orthopaedic Centre near Cairo, applying to become an orthopaedic specialist in 1942. Charnley returned to Manchester in 1946 at the Manchester Royal Infirmary as an honorary assistant orthopaedic surgeon and lecturer in orthopaedic surgery, and later as a consultant. In 1949, Charnley became a visiting orthopaedic surgeon at Wrightington Hospital. He began to work on the mobility of the hip in painful hip conditions due to arthritis. His discoveries in this field were made possible by his outstanding ability in engineering, and in working with materials. In 1961, Charnley established the Centre for Hip Surgery at Wrightington Hospital, where he pioneered and developed prostheses for hip replacement surgery, and studied the acceptance of artificial materials within bone and joint tissues. The hip replacement operation is now one of the most common operations performed in the UK. Material held by University of Manchester Library – full collection description.
Online Resource: London’s Pulse: Medical Officer of Health Reports 1848-1972. This collection features digitised reports of the UK Medical Officers of Health for the London area during the 19th and 20th centuries. These reports were compiled on an annual basis and include written information and statistical data on public health issues, such as infectious diseases, mortality rates, health services and environmental impacts on health. Selected reports are available from the period and the areas covered include the present City of London, the current 32 London boroughs and the predecessor local authorities for these areas. The reports also highlight the differences between different Medical Officers of Health and show how individual personality influenced their work and reporting style. Provided by the Wellcome Library.
Papers of Martindale, Louisa (1872-1966): Louisa Martindale was born in 1872 and studied at the London School of Medicine for Women and in Vienna, Berlin and Freiburg, obtaining her M.D. in London in 1906. She practised in Brighton and was founder of the New Sussex Hospital here in 1918, where she was Senior Honorary Surgeon. In 1921 she moved to London as a Consultant Surgeon and was Honorary Surgeon to the Marie Curie Hospital at Hampstead. During a visit to New York in 1919 she was a moving force behind the foundation of the Medical Women’s Federation and in 1931 she was elected President of that body. Martindale was a pioneer in the treatment of uterine cancer and fibroid growths in women through deep X-ray therapy. She died in 1966. Material held by the Wellcome Collection – full collection description.

HD/1/81: The minute book of the founders of the hospital, discussing the principles of kind treatment and moral management, dated 1842-1848. Image copyright © Archifau Sir Ddinbych / Denbighshire Archives.
Feature: Unlocking the Asylum: Cataloguing the North Wales Hospital Archive (August 2019).
Northern Ireland Hospitals Authority Archive (1948-1974): The collection consists of reports and monographs on the location, construction and administration of hospitals in Northern Ireland covering the period 1948 to 1974. Items include reports from The Northern Ireland Hospitals Authority, Hospital Management Committees, research organisations and central government. The archive constitutes the nucleus of the Northern Ireland Hospitals Authority library which passed to The Queen’s University of Belfast at the Authority’s demise in 1973. Queens University Medical Library continues to maintain an archive of material related to health and social services provision in Northern Ireland. Material held by Queen’s University Belfast Special Collections & Archives – full collection description.
One of our first attempts at archiving the RCN COVID-19 webpages using our digital archive. Image copyright © Royal College of Nursing Archives.
Feature: Creating a COVID-19 archive at the Royal College of Nursing (November 2020).
Florence Nightingale letters (1882-1883): Florence Nightingale, (1820-1910), nursing pioneer and reformer, is regarded as the founder of modern nursing. Born in Florence, Italy, she dedicated her life to the care of the sick and war wounded. In 1844, she began to visit hospitals; in 1850, she spent some time with the nursing Sisters of St. Vincent de Paul in Alexandria and a year later studied at the institute for Protestant deaconesses in Kaiserswerth, Germany. In 1854, she organized a unit of 38 nurses for service in the Crimean War. In 1860, she established the Nightingale School for nurse training at St. Thomas’s Hospital, London and in 1907 became the first woman to be given the British Order of Merit. This collection contains letters from Florence Nightingale to William Rathbone the MP for Caernarfonshire, concerning public health issues and the typhoid epidemic at Bangor in 1882. Material held by Archifdy Prifysgol Bangor / Bangor University Archives – full collection description.
Find out more
Follow us on Twitter @archiveshub and on Facebook
Join our mailing list: to receive updates about what is on the Hub and tips for using archives in your research, please visit our jiscmail list to sign up.
How to search the Archives Hub: https://archiveshub.jisc.ac.uk/using/.
Read more features
Explore more Online Resources












