This post is in response to a recent article in Code4Lib, ‘Thresholds for Discovery: EAD Tag Analysis in ArchiveGrid, and Implications for Discovery Systems‘ by M. Bron, M. Proffitt and B. Washburn. All quotes are from that article, which looked at the instances of tags within ArchiveGrid, the US based archival aggregation run by OCLC. This post compares some of their findings to the UK based Archives Hub.
Date
In the ArchivesGrid analysis, the <unitdate> field use is around 72% within the high-level (usually collection level) description. The Archives Hub does significantly better here, with an almost universal inclusion of dates at this level of description. Therefore, a date search is not likely to exclude any potentially relevant descriptions. This is important, as researchers are likely to want to restrict their searches by date. Our new system also allows sorting retrieved results by date. The only issue we have is where the dates are non-standard and cause the ordering to break down in some way. But we do have both displayed dates and normalised dates, to enable better machine processing of the data.
Collection Title
“for sorting and browsing…utility depends on the content of the element.”
Titles are always provided, but they are very varied. Setting aside lower-level descriptions, which are particularly problematic, titles may be more or less informative. We may introduce sorting by title, but the utility of this will be limited. It is unlikely that titles will ever be controlled to the extent that they have a level of consistency, but it would be fascinating to analyse titles within the context of the ways people search on the Web, and see if we can gauge the value of different approaches to creating titles. In other words, what is the best type of title in terms of attracting researchers’ attention, search engine optimisation, display within search engine results, etc?
Lower-level descriptions tend to have titles such as ‘Accounts’, ‘Diary’ or something more difficult to understand out of context such as ‘Pigs and boars’ or ‘The Moon Dragon’. It is clearly vital to maintain the relationship of these lower-level descriptions to their parent level entries, otherwise they often become largely meaningless. But this should be perfectly possible when working on the Web.
It is important to ensure that a researcher finding a lower-level description through a general search engine gets a meaningful result.
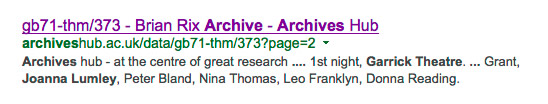
The above result is from a search for ‘garrick theatre archives joanna lumley’ – the sort of search a researcher might carry out. Whilst the link is directly to a lower -level entry for a play at the Garrick Theatre, the heading is for the archive collection. This entry is still not ideal, as the lower-level heading should be present as well. But it gives a reasonable sense of what the researcher will get if they click on this link. It includes the <unitid> from the parent entry and the URL for the lower-level, with the first part of the <scopecontent> for the entry. It also includes the Archives Hub tag line, which could be considered superfluous to a search for Garrick Theatre archives! However, it does help to embed the idea of a service in the mind of the researcher – something they can use for their research.
Extent
“It would be useful to be able to sort by size of collection, however, this would require some level of confidence that the <extent> tag is both widely used and that the content of the tag would lends itself to sorting.”
This was an idea we had when working on our Linked Data output. We wanted to think about visualizations that would help researchers get a sense of the collections that are out there, where they are, how relevant they are, and so on. In theory the ‘extent’ could help with a weighting system, where we could think about a map-based visualization showing concentrations of archives about a person or subject. We could also potentially order results by size – from the largest archive to the smallest archive that matches a researchers’ search term. However, archivists do not have any kind of controlled vocabulary for ‘extent’. So, within the Archives Hub this field can contain anything from numbers of boxes and folders to length in linear metres, dimensions in cubic metres and items in terms of numbers of photographs, pamphlets and other formats. ISAD(G) doesn’t really help with this; the examples they give simply serve to show how varied the description of extent can be.
Genre
“Other examples of desired functionality include providing a means in the interface to limit a search to include only items that are in a certain genre (for example, photographs)”.
This is something that could potentially be useful to researchers, but archivists don’t tend to provide the necessary data. We would need descriptions to include the genre, using controlled vocabulary. If we had this we could potentially enable researchers to select types of materials they are interested in, or simply include a flag to show, e.g. where a collection includes photographs.
The problem with introducing a genre search is that you run the risk of excluding key descriptions, because the search will only include results where the description includes that data in the appropriate location. If the word ‘photograph’ is in the general description only then a specific genre search won’t find it. This means a large collection of photographs may be excluded from a search for photographs.
Subject
In the Bron/Proffitt/Washburn article <controlaccess> is present around 72% of the time. I was surprised that they did not choose to analyse tags within <controlaccess> as I think these ‘access points’ can play a very important role in archival descrpition. They use the presence of <controlaccess> as an indication of the presence of subjects, and make the point that “given differences in library and archival practices, we would expect control of form and genre terms to be relatively high, and control of names and subjects to be relatively low.”
On the Archives Hub, use of subjects is relatively high (as well as personal and corporate names) and use of form and genre is very low. However, it is true to say that we have strongly encouraged adding subject terms, and archivists don’t generally see this as integral to cataloguing (although some certainly do!), so we like to think that we are partly responsible for such a high use of subject terms.
Subject terms are needed because they (1) help to pull out significant subjects, often from collections that are very diverse, (2) enable identification of words such as ‘church’ and ‘carpenter’ (ie. they are subjects, not surnames), (3) allow researchers to continue searching across the Archives Hub by subject (subjects are all linked to the browse list) and therefore pull collections together by theme (4) enable advanced searching (which is substantially used on the Hub).
Names (personal and corporate)
In Bron/Proffitt/Washburn the <origination> tag is present 87% of the time. The analysis did not include the use of <persname> and <corpname> within <origination> to identify the type of originator. In the Archives Hub the originator is a required field, and is present 99%+ of the time. However, we made what I think is a mistake in not providing for the addition of personal or corporate name identification within <origination> via our EAD Editor (for creating descriptions) or by simply recommending it as best practice. This means that most of our originators cannot be distinguished as people or corporate bodies. In addition, we have a number where several names are within one <origination> tag and where terms such as ‘and others’, ‘unknown’ or ‘various’ are used. This type of practice is disadvantageous to machine processing. We are looking to rectify it now, but addressing something like this in retrospect is never easy to do. The ideal is that all names within origination are separately entered and identified as people or organisations.
We do also have names within <controlaccess>, and this brings the same advantages as for <subjects>, ensuring the names are properly structured, can be used for searching and for bringing together archives relating to any one individual or organisation.
Repository
“Use of this element falls into the promising complete category (99.46%: see Table 7). However, a variety of practice is in play, with the name of the repository being embellished with <subarea> and <address> tags nested within <repository>.”
On the Archives Hub repository is mandatory, but as yet we do not have a checking system whereby a description is rejected if it does not contain this field. We are working towards something like this, using scripts to check for key information to help ensure validity and consistency at least to a minimum standard. On one occasion we did take in a substantial number of descriptions from a repository that omitted the name of repository, which is not very useful for an aggregation service! However, one thing about <repository> is that it is easy to add because it is always the same entry. Or at least it should be….we did recently discovery that a number of repositories had entered their name in various ways over the years and this is something we needed to correct.
Scope and content, biographical history and abstract
It is notable that in the US <abstract> is widely used, whereas we don’t use it at all. It is intended as a very brief summary, whereas <scopecontent> can be of any length.
“For search, its worth noting that the semantics of these elements are different, and may result in unexpected and false “relevance””
One of the advantages of including <controlaccess> terms is to mitigate against this kind of false relevance, as a search for ‘mason’ as a person and ‘mason’ as a subject is possible through restricted field searching.
The Bron/Proffitt /Washburn analysis shows <bioghist> used 70% of the time. This is lower than the Archives Hub, where it is rare for this field not to be included. Archivists seem to have a natural inclination to provide a reasonably detailed biographical history, especially for a large collection focussed on one individual or organisation.
Digital Archival Objects
It is a shame that the analysis did not include instances of <dao>, but it is likely to be fairly low (in line with previous analysis by Wisser and Dean, which puts it lower than 10%). The Archives Hub currently includes around 1,200 instances of images or links to digital content. But what would be interesting is to see how this is growing over time and whether the trajectory indicates that in 5 years or so we will be able to provide researchers with routes into much of the Archives Hub content. However, it is worth bearing in mind that many archives are not digitised and are not likely to be digitised, so it is important for us not to raise expectations that links to digital content will become a matter of course.
The Future of Discovery
“In order to make EAD-encoded finding aids more well suited for use in discovery systems, the population of key elements will need to be moved closer to high or (ideally) complete.”
This is undoubtedly true, but I wonder whether the priority over and above completeness is consistency and controlled vocabulary where appropriate. There is an argument in favour of a shorter description, that may exclude certain information about a collection, but is well structured and easier to machine process. (Of course, completeness and consistency is the ideal!).
The article highlights geo-location as something that is emerging within discovery services. The Archives Hub is planning on promoting this as an option once we move to the revised EAD schema (which will allow for this to be included), but it is a question of whether archivists choose to include geographical co-ordinates in their catalogues. We may need to find ways to make this as easy as possible and to show the potential benefits of doing so.
In terms of the future, we need a different perspective on what EAD can and should be:
“In the early days of EAD the focus was largely on moving finding aids from typescript to SGML and XML. Even with much attention given over to the development of institutional and consortial best practice guidelines and requirements, much work was done by brute force and often with little attention given to (or funds allocated for) making the data fit to the purpose of discovery.”
However, I would argue that one of the problems is that archivists sometimes still think in terms of typescript finding aids; of a printed finding aid that is available within the search room, and then made available online….as if they are essentially the same thing and we can use the same approach with both. I think more needs to be done to promote, explain and discuss ‘next generation finding aids’. By working with Linked Data, I have gained a very different perspective on what is possible, challenging the traditional approach to hierarchical finding aids.
Maybe we need some ‘next generation discovery’ workshops and discussions – but in order to really broaden our horizons we will need to take heed of what is going on outside of our own domain. We can no longer consider archival practice in isolation from discovery in the most general sense because the complexity and scale of online discovery requires us to learn from others with expertise and understanding of digital technologies.